You Need D
🌍 Melanin & Latitude
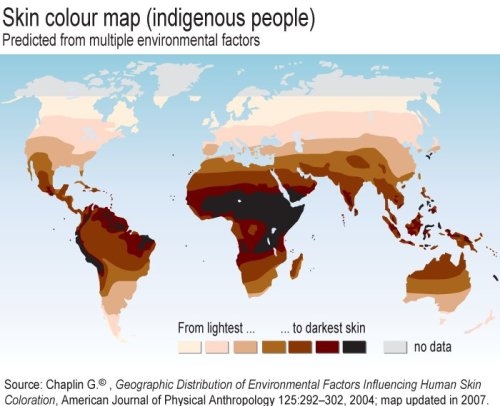
The richly pigmented skin of the first humans conferred a major protection against the African sun. Melanin--the dark pigment coloring skin, hair and the iris--blocks UV rays and offers a shield against sunburn and skin cancer.
However, what protects in one environment can restrict in another. Upon migrating away from the sun-drenched planes of Africa, Homo sapiens would have quickly developed a vitamin D deficiency. The weaker UV rays yielded lower vitamin D production in the skin of these northern explorers. As such, European latitudes incentivized a decrease in melanin production: increased penetration of UV rays leading to increased production of Vitamin D.
Vitamin D is essential to reproductive health. Low maternal levels of this vitamin are associated with a higher risk of pregnancy complications for the mother and low birth weights for the baby (Bodnar). Thus, those with lighter skin produced healthier and more numerous offspring (Wimalawansa). Humans who evolved to capture more UV rays at northern latitudes were reproductively dominant and offers one explanation for the light skin predominance in northern Europe.
👩🏼 Ready to Think? 👩🏾
Which of these two women is more likely to have a vitamin D deficiency: a light-skinned, pescatarian female living in Sweden or a dark-skinned female living in Saudi Arabia?
A person's level of vitamin D is multi-factorial, depending on UV exposure, skin pigmentation, cultural norms and diet, among others. Light skin allows easier penetration of UV rays, which would favor the Swedish woman; however, the Arabian peninsula is much closer to the equator and offers more direct sunlight, which would favor the Saudi woman. However, in Saudi Arabia women are required to don a burqa, often concealing every bit of their body except for the eyes. Even with ample UV potential, the Saudi woman likely receives no direct sun exposure. Contrast this with Scandinavians who, given the infrequency of warm, sunny weather, make every effort to catch some rays when the sun is out. Furthermore, the Swedish woman regularly consumes fish, one of the only natural dietary sources of vitamin D. Despite living near the equator, the Saudi woman is much more likely to be deficient in vitamin D than her Swedish counterpart.
✨ More than Bones
Historically, scientists learned about the function of vitamins by what happened when someone was severely lacking that vitamin. For vitamin C this was Scurvy. For vitamin D, this meant rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults, two forms of impaired bone mineralization. Those lacking vitamin D would suffer from bone pain, difficulty walking, bone deformities and even fractures.
Vitamin D plays an essential role in regulating levels of calcium and phosphate, two essential ingredients to mineralize bone. As such, vitamin D was hailed as the vitamin for strong, healthy bones. And it is. However, vitamin D receptors are located throughout the body, including the: intestine, cardiovascular system, brain, pancreas, and muscles.
From regulating cell replication to optimizing the immune system, vitamin D plays a role far beyond building and maintaining a healthy skeleton.
Roles of Vitamin D:
- Mineralizing bone
- Preventing falls and fractures
- Preventing cancer (i.e. breast, colon, prostate)
- Preventing cardiovascular disease
- Preventing autoimmune disease (i.e. Rheumatoid arthritis, Multiple sclerosis, psoriasis)
- Preventing insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome
- Preventing depression
Sources of Vitamin D
There are two environmental sources of Vitamin D: UVB-enabled skin production and dietary sources.
UVB ☀️
The sun's ultraviolet B rays enable synthesis of vitamin D in the skin. This is the body's principal source of vitamin D. Dosing of UVB varies based on person, place and time of year. For a light-skinned individual to maximize vitamin D synthesis, she needs up to 20 minutes of direct sunlight to exposed skin without use of sunscreen. Compare this to her dark-skinned friend who requires 3-6 times more sun exposure to achieve the same level of vitamin D production.
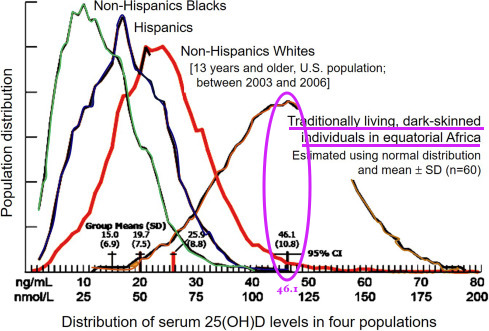
The average level of Vitamin D in blacks at northern latitudes is significantly lower than that of their matched white counterparts. Could a deficiency in vitamin D be responsible for discrepancies in cancer rates between blacks and whites living at the same northern latitude? Could vitamin D prevent replication of cancerous cells through its role in regulating the cell cycle? Whoa.
Remember to increase exposure to UVB gradually and never stay in the sun to the point of sunburn, which increases the risk for skin cancer!
Many factors influence sun-derived vitamin D production:
- Amount of melanin in skin
- Surface area of exposed skin
- Duration of exposure
- Intensity of sunlight (i.e. altitude)
- Zenith angle of the sun (i.e. time of day)
- Application of sunscreen (which blocks 95-98% of UVB)
- Presence of glass (e.g. windows in the home or car, which block UVB)
- Presence of clouds and pollution (which block UVB)
- Cultural norms (e.g. avoiding sunlight or traditional dress minimizing skin exposure)
However, due to geography and cultural practices, few people reach the optimal vitamin D range from sun exposure alone.
Diet 🐟🍄🍼
There are a limited number of foods which contain vitamin D, including: fatty fish (e.g. salmon, tuna and mackerel), mushrooms and vitamin D fortified foods (e.g. milk, orange juice and cereals). It's nearly impossible to obtain sufficient vitamin D from dietary sources given then relatively small amount contained in these foods. As such, most people need to consider supplementation of the vitamin.
Supplementation 💊
There are two forms of vitamin D supplements: D2 [Ergocalciferol] which requires a prescription and D3 [Cholecalciferol] which can be purchased over the counter. Although D2 requires a physician's prescription, D3 supplementation is more effective in increasing blood levels of vitamin D (Shieh). Furthermore, D3 has a longer half life than D2 (it hangs out in the body longer) and therefore has greater potential for metabolic activity (Alshahrani and Aljohani).
I recommend D3 over D2.
🎯 What's the Optimal Level of Vitamin D?
If you live in New York City, there is a 9 in 10 chance that you have a vitamin D deficiency, which is defined as a vitamin D level less than 20ng/mL. The range between 20-29ng/mL represents an insufficient level. And "normal" is greater than 30ng/mL. But you don't want to be normal; you want to be optimal.
Deficient <20ng/mL
Insufficient 20-29ng/mL
Normal >30ng/mL
Optimal ??? ng/mL
Just because a value of 30 is above the reference range for insufficiency does NOT mean this value is optimal for health. A level of at least 30ng/mL of Vitamin D is needed for proper bone mineralization. However, a higher level of vitamin D is needed for optimal immune function and cancer prevention, and an even higher level would be required for treatment of autoimmune disease and cancer (Wimalawansa).
So, the question remains: what level of vitamin D will maximize your body's performance? Our best guess would be the level of vitamin D under which the human body evolved thousands of years ago. The closest approximation would be looking at the vitamin D levels of modern-day equatorial Africans: 46ng/mL. Although different authorities continue to debate this optimal level, in my practice I recommend a concentration of at least 40ng/mL.
From Luxvolda et. al., modified by Wimalawansa. Wimalawansa reports that the serum Vitamin D concentration of equatorial Africans, 46 nmol/L, should be regarded as the true physiologic level for humans.
🤔 So Doc, How Much D Do I Need?
How much D do you need in order to hit 40ng/mL?
If you've ever been diagnosed with a vitamin D deficiency, I imagine your doctor prescribed 50,000 International Units [IU] of D2 once weekly for 8 weeks, followed by a maintenance dose of 2,000 IU daily. But, will a daily maintenance dose of 2,000 IU sustain a level of >40ng/mL? Doubt it. Plus, D2 is inferior to D3.
One over the counter brand offering 5,000 IU capsules of vitamin D3.
I recommend at least 5,000 IU of D3 daily when you're unable to get sufficient UVB exposure (October through May in New York City). However, there is only one way to ensure that your level is >40ng/mL ... Blood testing!
VITAMIN D TOXICITY
Vitamin D toxicity [blood levels greater than 150ng/mL] can occur from over supplementation, but would require scarfing down 40,000 IU or more daily for several months (Alshahrani and Aljohani)!
⚠️ Get Your Level Checked
The only way to confirm an optimal level of vitamin D is periodic blood testing. If your level is below 40ng/mL, your UVB exposure and/or the dose of your supplement needs to be increased.
Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D is the ideal blood test to check overall vitamin D status. Make sure your doctor is checking this level of vitamin D and not one of the others!
Works Cited
F. Alshahrani and N. Aljohani. "Vitamin D: Deficiency, Sufficiency and Toxicity" Nutrients 2013, 5(9), 3605-3616.
L.M. Bodnar, J.M. Catov, H.N. Simhan, M.F. Holick, R.W. Powers, J.M. Roberts "Maternal vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of preeclampsia" J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 92 (9) (2007), pp. 3517–3522
L.M. Bodnar, J.M. Catov, J.M. Zmuda, M.E. Cooper, M.S. Parrott, J.M. Roberts, et al. "Maternal serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are associated with small-for-gestational age births in white women" J. Nutr., 140 (5) (2010), pp. 999–1006
S.J. Wimalawansa. "Non-musculoskeletal benefits of vitamin D" J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 20 Sep 2016. pii: S0960-0760(16)30252-7.
S.J. Wimalawansa. "Vitamin D: Everything You Need to Know" 978-955-9098-94-2 Karunaratne & Sons, Homagama, Sri Lanka (2012)
Shieh A. et. al. "Effects of High-Dose Vitamin D2 Versus D3 on Total and Free 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Markers of Calcium Balance" J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Aug: 101(8):3070-8.