Symbiosis
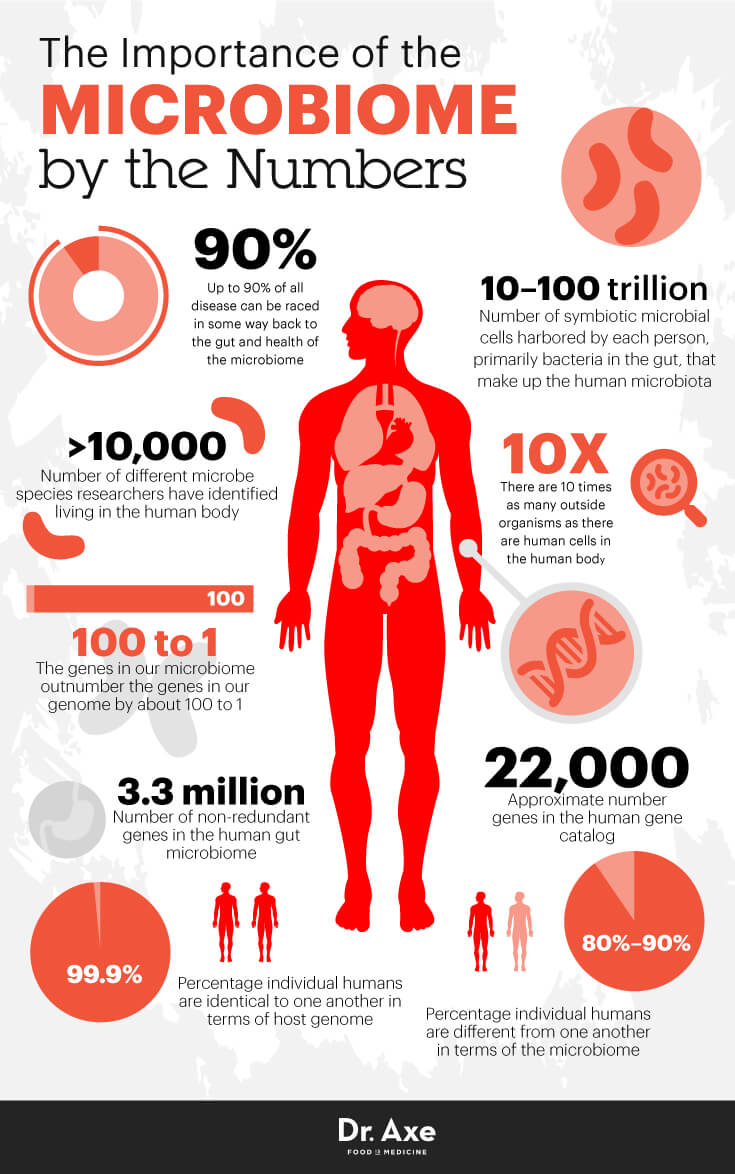
Over 100 trillion
Over 100 trillion microorganisms inhabit your body. In essence, you are a vehicle for bacteria, viruses, yeast, protozoa, fungi and archaea.
So, how many cells are actually yours? In other words, how many of your body's cells are derived from your DNA? Approximately 10 trillion. Yes, this means that bacterial cells outnumber your own cells by a factor of 10:1.
You are only 10% human.
Human Microbiome Project
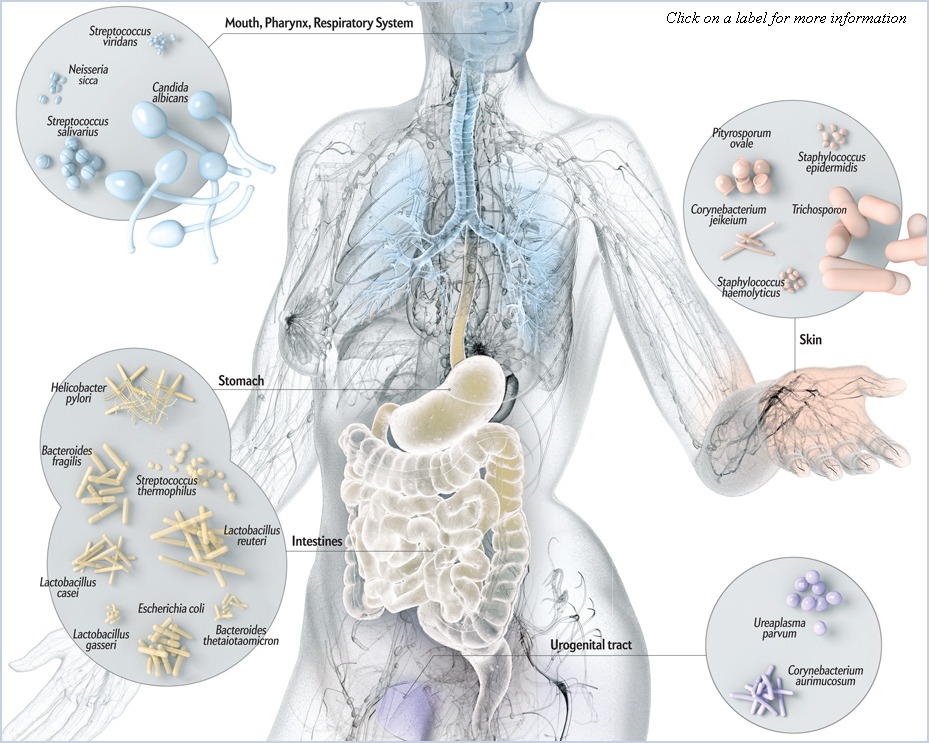
The Human Microbiome Project, led by the US National Institutes of Health, endeavors to identify and characterize these 100 trillion microorganisms hosted by the human body.
There are 100 times the number of genes in the human microbiome than the human genome; the Human Microbiome Project is far more ambitious than the Human Genome Project.
The project focuses on investigating five microbiomes:
- Skin
- Nose/Lung
- Mouth
- Gut
- Vagina
The goal of this project is to better understand the relationship between microbiomes and diseases.
For instance, do people with Irritable Bowel Syndrome have different gut bacteria than people without IBS? If so, are these bacteria a cause or a result of IBS? Could these gut bacteria be altered to treat IBS?
Knowledge of the human microbiomes is just beginning to blossom.
Perhaps not so surprising, the bacterial population of the skin is very different from the mouth, both of which are different from the bacteria living in the gut. Different environments drive different bacteria to thrive.
Survival of the fittest bacteria
One fascinating finding of the project thus far is that biomes between individuals can vary significantly. For instance, the bacteria colonizing the gut of one person can be very different from his neighbor's gut microbiome, even if both individuals are in good states of health. What drives these differences--genetic predisposition vs environment--remains to be determined.
From bioxplorer.com
Hygiene
Consider your hygienic practices:
Antibiotics
Mouthwash
Hand sanitizer
Vaginal & anal douching
Is this how you should treat your microbiomes?
In theory, the goal of these hygienic strategies is to eliminate "bad" bacteria. However, are you also removing "good" bacteria? Certainly. Antibiotics, which kill indiscriminately, are the biggest culprit.
Think twice before asking your physician to prescribe antibiotics unless you actually have a bacterial infection. When taking antibiotics, make a concerted effort to consume fresh vegetables and fruits to promote repopulation of your gut microbiome.
Symbiosis
Are you shuddering in disgust at the thought of a constant bacterial fiesta on your body?
The antimicrobial industry has misled you to believe that bacteria are your enemy. In fact, quite the opposite is true: bacteria are your friends. Quite sincerely, bacteria are your best friends.
Symbiosis is a state of coexistence between organisms.
The bacteria of your microbiomes play essential roles in the function of your body; in return, you provide shelter and nutrients for your microorganisms. This is symbiosis.
Derived from Greek, sym-biosis literally means "living together". Over millions of years of evolution, organisms small and large recognized the benefit of combining resources.
The clownfish feeds on organisms that have the potential to harm the sea anemone. The feces of the clownfish provides nutrition for the sea anemone. The clownfish can hide from predators within the sea anemone, which possesses stinging cells to which the clownfish is immune. Image from wikipedia.
Mike Petegorsky & Sadie. Humans and canines demonstrate a symbiotic relationship. Sadie receives shelter and food from Mike. Mike receives protection and companionship from Sadie.
Colonization
Where did your microorganisms come from?
The single most important event in development of the human microbiome is passage through the vaginal canal during birth. The first bacteria to colonize the digestive tract and skin of the newborn comes from the mother's vaginal flora. For this reason, c-section should only be performed if absolutely necessary.
Next week, we will dive deeper into the microbiome of the digestive tract. Stay tuned!
From https://draxe.com/microbiome/
Cover image illustration by Charis Tsevis.
Sources
http://bioxplorer.com/human-microbiome/
https://draxe.com/microbiome/
http://whyfiles.org/2015/eight-ways-microbes-keep-you-healthy/